In the fast-paced world of business, entrepreneurs need to be on top of their game to stay competitive. One key aspect that cannot be overlooked is efficient warehousing. After all, the success of your supply chain hinges on it. But fear not because the solution is simple – a cutting-edge warehouse management system.
From the sourcing of raw materials to the final delivery of the product, the supply chain is a continuous flow of goods and services. The storage of these items is critical to the process and plays a pivotal role in logistics. This is where a robust ERP warehouse management system (WMS) comes in, eliminating bottlenecks such as volatile supplies and delays.
However, before delving deeper into the intricacies of WMS, let’s establish a foundational understanding of the fundamental aspects of warehousing.
What is Warehouse Management?
Warehouse management refers to the efficient and systematic control of various operations within a warehouse. It involves overseeing and optimizing the processes related to inventory management, storage, picking, packing, and shipping of goods. The primary goal of warehouse management is to ensure that the right products are in the right place at the right time, minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency throughout the supply chain.
Benefits of Warehouse Management
Implementing a Warehouse Management System (WMS) offers numerous benefits that significantly enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and overall performance of warehouse operations. Some of the key benefits include:
- Enhanced inventory accuracy with real-time tracking
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Maximized warehouse space with intelligent storage strategies
- Accurate order fulfillment
- Improved visibility and control with real-time insights
- Lowered operational expenses related to labor, inventory, and fulfillment
- Prompt and accurate order deliveries that enhance customer experience
Principles of Warehouse Management
Effective warehouse management involves several principles to ensure smooth operations and optimized efficiency. Here are three key principles:
1. Organization and Layout Optimization
- Efficiently organizing the warehouse layout is crucial. Design the floor plan to minimize travel time for picking, packing, and storing goods.
- Implement logical categorization and labeling systems for inventory items to facilitate easy identification and retrieval.
- Utilize space wisely by employing shelving, racking, or automated storage systems to maximize storage capacity.
2. Inventory Management and Control
- Maintain accurate inventory records through the use of a robust inventory management software.
- Conduct regular cycle counts and reconcile inventory to prevent discrepancies and avoid stockouts or overstock situations.
- Implement inventory forecasting techniques to anticipate demand and adjust stock levels accordingly.
3. Optimize Operational Processes
- Streamline warehouse workflows by establishing efficient receiving, storing, picking, and shipping procedures.
- Implement lean management techniques to reduce waste, minimize errors, and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Use technology such as barcode scanners, RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification), or WMS (Warehouse Management Systems) to automate and optimize processes.
What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System, or simply e-commerce WMS, is a software application that helps manage and optimize the operations of a warehouse by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels. From the moment a shipment enters the warehouse to the moment it leaves, the WMS tracks every step and keeps everything running smoothly.
But the WMS is more than just a tracking system. It’s a mastermind of efficiency that maximizes labor and space utilization while coordinating and optimizing resource usage and material flows. In short, it’s the secret weapon that allows companies to operate warehouses like a well-oiled machine. With a fully integrated cloud-based WMS, you can easily achieve 100% inventory data accuracy, allowing you to process orders and replenish goods more efficiently.
Inventory Management vs Warehouse Management
Inventory management and warehouse management are interconnected but distinct aspects of e-commerce operations. Inventory management involves overseeing the quantity, location, and movement of goods throughout the supply chain to meet customer demand efficiently, minimizing costs, and optimizing stock levels.
Warehouse management, on the other hand, focuses on the physical storage, organization, and handling of inventory within a warehouse facility, ensuring streamlined operations, efficient picking, packing, and shipping processes, and the utilization of space and resources to facilitate smooth logistics operations.
While inventory management deals with the broader supply chain, warehouse management specifically concentrates on the activities within the warehouse premises to ensure effective handling and movement of inventory. Both are integral parts of logistics and supply chain management, working together to ensure timely and accurate delivery of products to customers.
Types of Warehouse Management Systems
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) come in various types, each catering to specific needs and operational requirements within the warehouse. Here are some common types of Warehouse Management Systems:
- Standalone WMS: A standalone WMS operates independently and is not integrated with other systems like ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). It focuses solely on warehouse operations, offering functionalities such as inventory tracking, order picking, packing, and shipping.
- ERP-Integrated WMS: Many WMS are integrated within broader ERP systems. These systems combine WMS functionalities with other business processes like accounting, human resources, and customer relationship management. This integration ensures seamless data flow between different departments within an organization.
- Cloud-Based WMS: Cloud-based WMS solutions are hosted on remote servers and accessed through the Internet. They offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility from any location with an internet connection. Cloud-based systems often come with subscription models, reducing the need for upfront infrastructure investments.
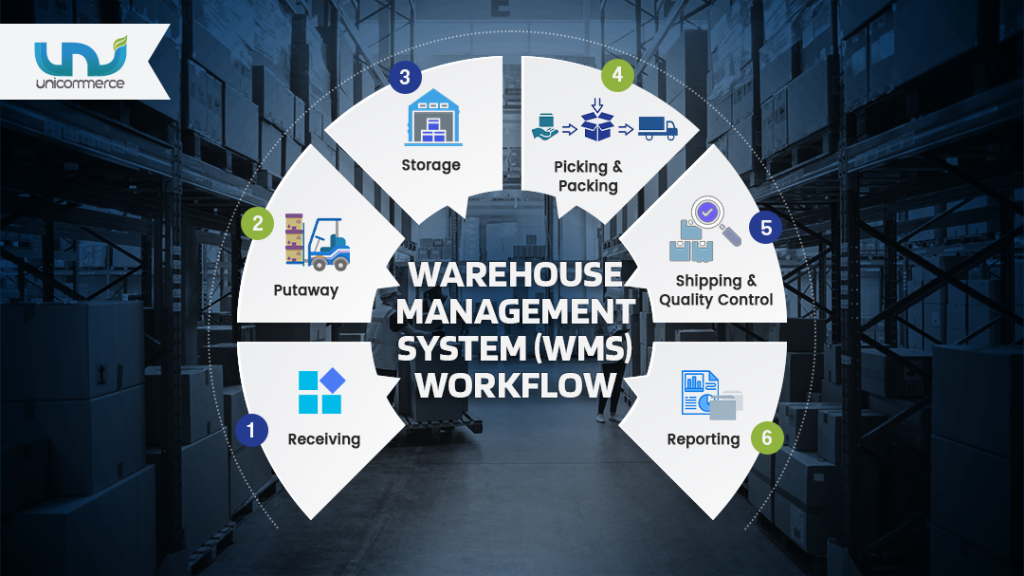
Understanding the Workflow of a Warehouse Management System (WMS)
Process of Warehouse Management System are:
- Step #1: Receiving
- Step #2: Putaway
- Step #3: Storage
- Step #4: Picking and Packing
- Step #5: Shipping and Quality Control
- Step #6: Reporting
It’s important to understand the workflow of a warehouse management system (WMS) in order to optimize operations and improve efficiency. The typical workflow of a WMS includes the following core functionalities:
Step #1: Receiving
Receiving Workflow in Warehouse Management System –
- Pre-receiving
- Receiving & Unloading Stocks
- Inspection of received inventory
- Putaway
The first step in a warehouse management system is “Receiving.” This step ensures that the right product has been received in the right quantity, quality, and location and at the right time. To make this process even more efficient, a powerful warehouse management system allows businesses to input key purchase order details such as delivery and expiry dates, as well as vendor information. Once everything has been received and verified, a Goods Received Note (GRN) is created to confirm that all the goods have indeed been received.
Step #2:Putaway
Putaway Workflow in Warehouse Management System –
- Operator to scan barcode
- Transfer goods to location
- Scan and puts away in location
- Putaway confirmed
After the receiving process is complete, the goods need to be moved from the receiving area to their designated storage locations. This process is called putaway, and it is critical to ensure that products are handled correctly during this process to avoid costly damages.
Fortunately, a well-designed warehouse management system (WMS) can help businesses avoid these issues by facilitating the creation of efficient putaway processes that optimize operational productivity.
Step #3: Storage
Storage is a vital aspect of any business that ensures the proper placement of goods in the warehouse. The goal is to maximize storage efficiency while minimizing errors and damage to goods. But how can this be achieved? That’s where Shelf Management comes into play.
It involves the strategic arrangement of goods on shelves to optimize space utilization, minimize errors, and prevent damage to products. By properly executing this process, businesses can maximize their available storage area and increase productivity.
Step #4: Picking and Packing
Picking & Packing Workflow in Warehouse Management System –
- Receive
- Process
- Pick
- Pack
- Inventory
- Ship
Picking and packing are integral components of order fulfillment, and optimizing these processes can significantly reduce costs. When order details are received, they can be passed on to warehouse staff through a picklist generated using WMS. This list provides essential details to the picker, including order information, item details, shelf locations, barcode scanning, and batch/lot numbers.
Suggested reading – What is order picking in a warehouse?
The products are selected from the warehouse using handheld devices that scan each item’s barcode. Once the items have been picked, they are packed in a way that minimizes the risk of damage during transportation. Shipping labels are generated, and an invoice is created to accompany the order.
Suggested reading – What is the packing and dispatch process in a warehouse?
Step #5: Shipping and Quality Control
Shipping and Quality Control in Warehouse Management System –
- Receiving
- Shelving Putaway
- Picking Kitting
- Packing
- Shipping
The shipping and quality control (QC) process marks the end of the journey for goods. This step is particularly important, as it has a direct impact on the customer experience. Incorrectly shipping products to the wrong customers can result in negative feedback.
To avoid such scenarios, it is important to have robust QC measures in place, such as order verification, packing inspection, barcode scanning, weighing checks, etc. With automated WMS software, this process also gets automated, simplifying the order routing process.
What are the Benefits of Deploying a Centralized Warehouse Management System?
Let us walk you through the benefits of WMS so that you can understand its significance in streamlining your e-commerce operations! Top Benefits of Deploying a Centralized Warehouse Management System –
- Better Inventory Control with Quick Dispatch Time
- Reduced Manpower Costs and Errors
- Improved Auditing and Security
- Simplified Billing and Taxation Management
- Enhanced Customer Experience
- Increased Scalability and Flexibility
1. Better Inventory Control with Quick Dispatch Time
Inventory management is critical to the success of any business, particularly in the retail industry. For this, you need an efficient WMS that can consolidate and sort inventory quickly. This allows for bulk order processing and reduces order preparation time, resulting in quick dispatch of orders.
Implementing a WMS also provides access to detailed information on the location and status of each Stock Keeping Unit (SKU), including which batch it belongs to and its location within the warehouse. Barcoding is a commonly used identification method whereby each item is assigned a unique code that can be scanned or tracked as it moves through the warehouse.
With this information readily available, businesses can make informed decisions about inventory levels and restocking, which can help prevent stockouts and overstocking.
2. Reduced Manpower Costs and Errors
A powerful warehouse management system (WMS) can significantly reduce manpower costs and minimize errors in your warehouse operations. This is achieved through the automation of various functions, including inventory tracking, sorting, picking, and order processing.
With a WMS in place, your warehouse can also benefit from systematic inventory placement and quality checks, which can further reduce the risk of manual errors while enhancing overall efficiency. One of the key advantages of using a WMS is that it allows you to optimize both inward and outward warehouse operations.
This ensures that only high-quality, accurate products are delivered to end customers, preventing the delivery of defective products and ultimately reducing customer complaints.
3. Improved Auditing and Security
Auditing and security are crucial components of any warehouse management system. The sheer amount of inventory and transactions taking place on a daily basis can make it difficult to keep track of everything, let alone prevent theft or loss of goods. That’s why most warehouse management systems enable multiple employees to use the software while also linking specific users to specific transactions.
This creates a level of transparency and accountability that is essential for maintaining a secure and efficient warehouse. With each transaction tied to a specific employee, it becomes much easier to pinpoint any issues that may arise.
4. Simplified Billing and Taxation Management
A warehouse management system (WMS) is more than just a tool for inventory management. With a reliable WMS in place, you can streamline your billing process, which is a critical aspect of any business. Failure to manage your bills correctly can result in significant losses.
Fortunately, most WMS solutions come with pre-integrated third-party apps that can improve your ability to manage bills from a single screen. In addition to simplifying the billing process, an advanced WMS can also help you comply with government taxation standards by streamlining the tax calculation process for invoices.
5. Enhanced Customer Experience
Customers are the lifeblood of any business, and a centralized warehouse management system can help you focus on improving your customer’s buying journey and enhance their overall experience.
Businesses can quickly and accurately process customer orders and track the progress of each order from start to finish. This allows for timely and accurate communication with customers regarding order status, shipment tracking, and delivery times, which can greatly enhance the customer experience.
6. Increased Scalability and Flexibility
As your business grows, so will your warehouse management needs. With a centralized WMS in place, you can easily scale your operations to accommodate changes in demand, seasonality, or expansion into new markets.
A WMS can also provide flexibility in managing different types of products and order fulfillment models, such as dropshipping or third-party logistics, allowing businesses to adapt to changing customer demands and preferences.
What are the Features of a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A well-organized and structured warehouse with reliable and efficient performance is a huge asset for retail business. Here are the essential WMS features that can help you attain operational capabilities:
- Batch Management
- Cycle Count
- Shelf Management
- Bundle Management
- Barcode Scanning
- Returns Management
1. Batch Management
Batch management is an important feature of a warehouse management system that helps to manage and track inventory based on batches or groups. Batches represent distinct collections of products that share common characteristics such as manufacturing dates, expiration dates, or production lots. This feature is particularly useful in industries where products have a limited shelf life, such as the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics industries.
By grouping inventory into batches, businesses can minimize the amount of waste produced from expired or spoiled inventory. Additionally, batch management allows for the implementation of expiry management methods like FIFO (first in, first out) and FEFO (first expiry, first out). These methods enable stock rotation based on manufacturing and expiry dates, which helps to prevent the buildup of old inventory and avoid any potential damage from prolonged storage.
2. Cycle Count
Do you remember the days of the dreaded annual inventory count that would take forever? Well, thanks to the cycle count feature in Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), those days are long gone!
With regular inventory counts on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, businesses can now maintain accurate records, avoid stockouts, and optimize their warehouse operations. And the best part? Businesses can now have real-time updates on their day-to-day operations, making their supply chain management more efficient than ever before.
3. Shelf Management
Shelf management is an essential component of effective warehouse operations. It refers to the process of organizing and arranging products on shelves in a way that maximizes space and ensures efficient picking and restocking. Proper shelf management can significantly improve the overall productivity of a warehouse.
One way to achieve optimal shelf management is by using a robust Warehouse Management System (WMS). A WMS can assist in identifying the most suitable storage location for each product based on its attributes, such as size, weight, and demand frequency. This helps to ensure that products are arranged in a logical order, minimizing the time taken to locate them during picking and reducing errors.
4. Bundle Management
Product bundling is a popular sales strategy in which multiple SKUs are packaged together and sold as a combo pack to customers. While bundling offers benefits such as increased sales and customer satisfaction, it can be challenging to manage the various processes involved, from monitoring product availability to managing inventory for multiple sales channels.
The Bundle Management feature of a WMS can help to streamline these processes by allowing businesses to define bundle products as a group of individual SKUs, with each SKU being tracked individually. This enables businesses to monitor the availability of each SKU, ensuring that bundles are only created when all the SKUs are in stock.
5. Barcode Scanning
Barcodes are machine-readable representations of numeric and alphanumeric characters, typically consisting of bars and spaces. Barcodes offer several benefits in warehouse management, including improved accuracy, efficiency, and productivity.
The advanced barcoding feature provided by the WMS allows for the capture of accurate and intricate details of inventory at the item, SKU, and batch levels. This ensures that each item is uniquely identifiable and traceable, making it easier for businesses to track inventory movements, identify stock levels, and ensure timely replenishment.
6. Returns Management
With the rise of online shopping, customers have come to expect an easy and hassle-free returns process, which puts pressure on retailers to provide a seamless experience. To meet this demand, businesses require a robust Warehouse Management System (WMS) that can efficiently handle returns by simplifying the entire process, from authorizing returns to processing refunds or replacements.
Furthermore, the WMS returns feature allows businesses to manage e-commerce returns from various channels to multiple warehouses using a single system. For instance, if an order was processed from warehouse A, the return can be directed to warehouse B, which may be closer to the customer. This functionality simplifies the returns process, and minimizes potential errors and delays associated with handling returns across multiple platforms.
Factors to Consider When Selecting the Right Warehouse Management System for Your Business
Now that you know why a WMS is important, here are the key factors to consider when selecting the right WMS for your business:–
- Centralization of Multi Warehouse Inventory Management
- Real-Time and Customizable Reporting
- Third-party Integrations
- Virtual Multiple Warehouse Inventory Management
1. Centralization of Multi Warehouse Inventory Management
As customer demands continue to grow, businesses are exploring new ways to manage their operations in multiple warehouses simultaneously while maintaining a centralized view. Therefore, first and foremost, the WMS of your choice should centralize key tasks, such as automated stock level management, location allocation across multiple warehouse sites, real-time e-commerce inventory management, automated purchase management, shipment routing and tracking, and order management from multiple points of sale.
2. Real-Time and Customizable Reporting
Next, you need real-time information access about what’s going on in your warehouse to manage stock inventory effectively. You require a bird’s eye view of which stock units are in demand and which haven’t moved at all, geographic market-specific demand variations, and seasonal trends.
You should also be able to generate customizable reports to analyze inventory status and strategize warehouse utilization. An online multi-warehouse management system can enable you to achieve this, as the information remains remotely accessible and available in real-time.
3. Third-party Integrations
By integrating the WMS with other third-party applications, businesses can streamline various processes such as logistics, marketplace management, accounting, sales and CRM, and more.
A smart WMS should provide sophisticated tech stack solutions that seamlessly integrate with other software systems used in your business. Not only can this save time and resources, but it can also provide a more complete picture of your business operations.
4. Virtual Multiple Warehouse Inventory Management
Unutilized or under-utilized warehouse space increases your inventory carrying cost and burdens your value chain, even when you have a network of multiple warehouses to match market demand. To address this issue, you need a multi-warehouse management system that gives you a complete virtual view of warehouse space.
A virtual multiple warehouse management system allows you to manage your inventory across multiple warehouses as if they were one. You can view all your warehouses’ inventory levels in real-time and manage them from a centralized location.
Future-Proof your Business with Advance WMS!
An effective warehouse management system (WMS) enables you to perform plenty of tasks with utmost efficiency and accuracy. It also helps you ensure that your business is equipped to handle the challenges of tomorrow.
From optimizing inventory management to enhancing order fulfillment, a WMS can help you achieve operational excellence and drive growth. So what are you waiting for? Go ahead and deploy a robust WMS technology in your system today and reap the benefits of automation.
See how to improve Inventory Visibility & accuracy with E-commerce focused Warehouse Management System –
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How long does it take to implement a Warehouse Management System?
Ans: The time it takes to implement a Warehouse Management System can vary depending on the size and complexity of the warehouse, as well as the specific needs of the business. However, implementation can typically take six to eight months.
Q2. Can a Warehouse Management System be customized to meet specific business needs?
Ans: Yes, many Warehouse Management Systems can be customized to meet the specific needs of a business. This can include adding new features, modifying existing workflows, or integrating with other software.
Q3. What types of businesses can benefit from using a Warehouse Management System?
Ans: Any business that has a warehouse or distribution center can benefit from using a Warehouse Management System. This includes businesses in industries such as retail, manufacturing, wholesale distribution, and logistics.
Explore our platforms:
Related read –
- FMCG Industry Challenges & Solutions in India
- Top Essential WMS Features for Unleashing Operational Capabilities
- Why Warehouse Management System is important for Supply Chain?
- Logistics vs Supply Chain Management
- What is Order Picking?
- E-commerce Apparel Industry – Trends, Challenges & Solutions
- Footwear Industry in India – Trends, Challenges & Solutions
- Healthcare Industry in India – Trends, Challenges, Opportunities & Solutions
- Why Should you Deploy a Warehouse Management System?